International Myopia Conference 2017 Part 1
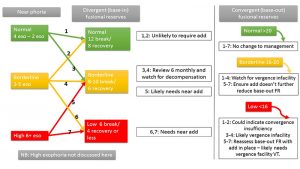
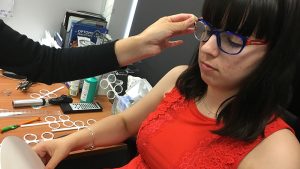
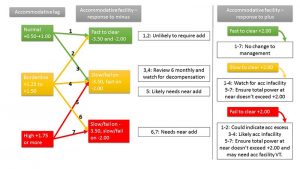
The session topics covered prevalence, progression and risk factors of myopia, mechanisms such as light exposure and visual pathways, optical and pharmacological methods of myopia control, genetics, clinical trial considerations, myopic eye shape and accommodation and binocularity.